FMA Protraction Device: Complete Guide to Midfacial Advancement
The field of airway orthodontics continues to evolve with innovative devices that address both functional and aesthetic concerns. One of the most exciting developments is the FMA (Facemask Appliance) protraction device, which represents a significant advancement in non-surgical midfacial development and airway improvement.
What Is the FMA Protraction Device?
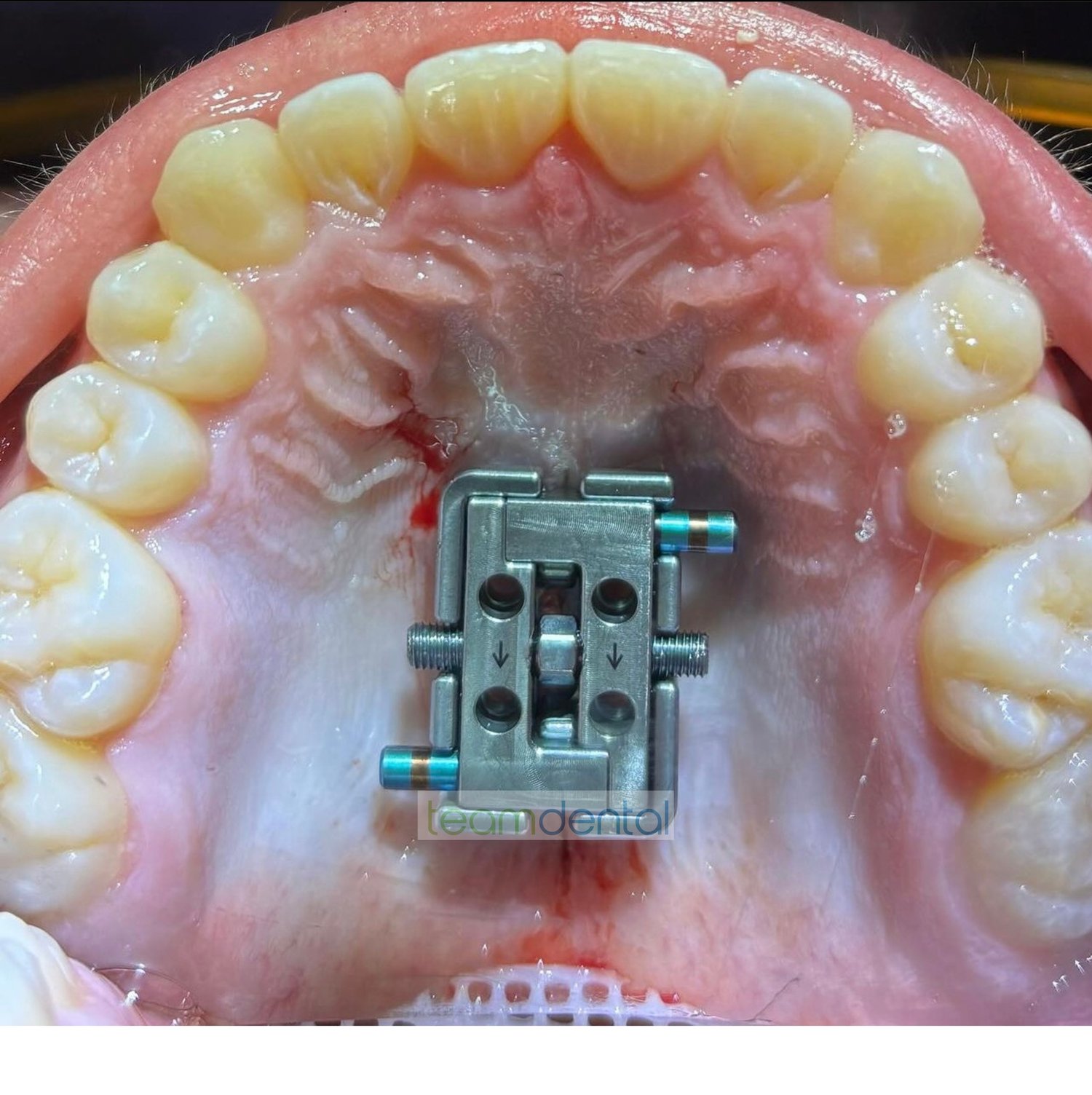
The FMA protraction device is a sophisticated orthopedic appliance designed to advance the midface (maxilla) forward through controlled protraction forces. Unlike traditional facemasks that rely primarily on dental anchorage, the FMA system utilizes bone-anchored expansion devices like the FME (Facegenics Midface Expander) to achieve true skeletal movement.
This innovative approach combines maxillary expansion with facial protraction, creating a comprehensive treatment that can address multiple issues simultaneously:
- Narrow palate and constricted airways
- Retruded midface and poor facial balance
- Class III malocclusion (underbite)
- Sleep-disordered breathing
- Aesthetic concerns related to midface deficiency
How Does Midfacial Advancement Work?
Midfacial advancement through the FMA device operates on well-established orthopedic principles:
1. Skeletal Anchorage
The FMA connects to bone-anchored expanders (like the FME) rather than relying on teeth for anchorage. This allows for:
- More predictable skeletal movement
- Reduced unwanted dental side effects
- Greater force application capability
- More stable long-term results
2. Controlled Protraction Forces
The device applies gentle, continuous forward pressure on the maxilla through:
- Elastic chains or springs
- Adjustable force vectors
- Distributed load application
- Gradual tissue adaptation
3. Suture Mobilization
The protraction forces work to:
- Stimulate bone formation at suture sites
- Encourage forward growth of the midface
- Improve facial proportions and balance
- Enhance airway dimensions
The Science Behind Airway Orthodontics
The connection between facial structure and airway function is fundamental to understanding why midfacial advancement can be so transformative.
Anatomical Relationships
- Nasal Floor: The maxilla forms the floor of the nasal cavity
- Airway Volume: Forward maxillary position increases nasal airway space
- Tongue Position: Improved maxillary position provides better tongue space
- Soft Tissue Support: Advanced midface supports facial soft tissues
Functional Benefits
Patients undergoing FMA treatment often experience:
- Improved nasal breathing
- Reduced mouth breathing
- Better sleep quality
- Enhanced facial aesthetics
- Improved oral function
FMA vs. Traditional Protraction Methods
| Aspect | FMA Device | Traditional Facemask |
|---|---|---|
| Anchorage | Bone-anchored (FME/MSE) | Dental anchorage |
| Force Application | Skeletal protraction | Dental-skeletal mixed |
| Age Range | Children and adults | Primarily children |
| Treatment Duration | 6-12 months | 12-18 months |
| Stability | High skeletal stability | Variable stability |
| Comfort | Improved patient comfort | Traditional headgear discomfort |
Who Can Benefit from FMA Treatment?
The FMA protraction device can be beneficial for various patient populations:
Children and Adolescents
- Class III malocclusion (underbite)
- Maxillary deficiency
- Narrow palate with midface retrusion
- Early intervention for facial growth guidance
Adults
- Mild to moderate maxillary deficiency
- Airway improvement goals
- Non-surgical facial enhancement
- Alternative to orthognathic surgery
Specific Conditions
- Sleep-disordered breathing: Improved airway dimensions
- Aesthetic concerns: Enhanced facial balance and proportion
- Functional issues: Better chewing, speaking, and breathing
- TMJ problems: Improved jaw positioning and function
The Treatment Process
FMA treatment typically follows a structured protocol:
Phase 1: Evaluation and Planning
- Comprehensive airway assessment
- 3D imaging and analysis
- Treatment planning and goal setting
- Patient education and consent
Phase 2: Expansion (if needed)
- FME or MSE placement for palatal expansion
- Gradual widening of the maxilla
- Suture loosening and preparation for protraction
- Monitoring of expansion progress
Phase 3: Protraction
- FMA device fitting and adjustment
- Gradual application of protraction forces
- Regular monitoring and adjustments
- Patient compliance and comfort optimization
Phase 4: Retention and Stabilization
- Gradual force reduction
- Retention appliance placement
- Long-term stability monitoring
- Final outcome assessment
Expected Outcomes and Results
Patients undergoing FMA treatment can expect several positive changes:
Facial Aesthetics
- Improved profile: Better facial balance and proportion
- Enhanced midface: More prominent cheekbones and support
- Balanced features: Harmonious facial relationships
- Smile enhancement: Wider, more attractive smile
Functional Improvements
- Breathing: Easier nasal breathing and reduced congestion
- Sleep: Better sleep quality and reduced snoring
- Oral function: Improved chewing, swallowing, and speaking
- Comfort: Reduced jaw pain and tension
Airway Benefits
- Increased volume: Larger nasal and pharyngeal airways
- Reduced resistance: Easier airflow during breathing
- Better oxygenation: Improved oxygen delivery during sleep
- Symptom relief: Reduction in sleep apnea symptoms
Considerations and Limitations
While the FMA device offers significant advantages, there are important considerations:
Patient Selection
- Age factors: Best results in growing patients, but adults can benefit
- Severity limits: Severe cases may still require surgical intervention
- Compliance needs: Success depends on consistent device wear
- Realistic expectations: Understanding achievable outcomes
Treatment Challenges
- Adaptation period: Initial discomfort and adjustment time
- Compliance requirements: Daily wear and maintenance
- Monitoring needs: Regular professional supervision
- Individual variation: Results vary based on patient factors
The Future of Midfacial Advancement
The FMA protraction device represents a significant step forward in non-surgical facial development. As technology continues to advance, we can expect:
Technological Improvements
- More precise force application systems
- Better patient comfort features
- Enhanced monitoring capabilities
- Improved treatment predictability
Expanded Applications
- Broader age range treatment options
- Integration with other airway therapies
- Combination with sleep medicine protocols
- Enhanced aesthetic outcomes
Choosing the Right Provider
Success with FMA treatment depends heavily on provider expertise:
Key Qualifications
- Specialized training: Specific FMA device certification
- Experience: Track record with protraction cases
- Comprehensive approach: Understanding of airway and facial development
- Technology access: Modern imaging and planning tools
Questions to Ask
- How many FMA cases have you treated?
- What are the expected outcomes for my specific case?
- What are the risks and potential complications?
- How will progress be monitored and adjusted?
- What is the total treatment timeline and cost?
Integration with Comprehensive Care
The FMA device works best as part of a comprehensive treatment approach:
Multidisciplinary Team
- Orthodontist: Device placement and monitoring
- Sleep specialist: Airway assessment and sleep study evaluation
- Myofunctional therapist: Muscle retraining and function optimization
- ENT specialist: Nasal and airway evaluation
Complementary Therapies
- Myofunctional therapy: Proper tongue and breathing patterns
- Sleep hygiene: Optimizing sleep environment and habits
- Breathing exercises: Nasal breathing training
- Postural therapy: Addressing head and neck alignment
Cost Considerations and Value
FMA treatment represents a significant investment in health and quality of life:
Treatment Costs
- Device and placement: $8,000 - $15,000
- Monitoring and adjustments: $2,000 - $4,000
- Complementary therapies: $1,000 - $3,000
- Total investment: $11,000 - $22,000
Value Proposition
- Non-surgical alternative: Avoiding more invasive procedures
- Comprehensive benefits: Addressing multiple issues simultaneously
- Long-term results: Stable, lasting improvements
- Quality of life: Better breathing, sleep, and appearance
Conclusion
The FMA protraction device represents a paradigm shift in how we approach midfacial deficiency and airway problems. By combining the benefits of skeletal expansion with controlled protraction forces, this innovative system offers patients a non-surgical path to improved facial balance, better breathing, and enhanced quality of life.
For patients who have been told that surgery is their only option for significant facial change, the FMA device opens new possibilities. The key to success lies in proper patient selection, expert application, and comprehensive care. For those who are good candidates, this revolutionary device can truly be life-changing.